
Metaphysics of sound
Learning from the Ancient Egyptian Book of Death Art, Symbols and Signs, Power of Mind, Mantras, defaultMystical Traditions and Metaphysics of Sound
True Name of god and Ancient symbols and frequencies
by Nataša Pantović
Pulsation, vibration, rhythm exists everywhere as Akasha / Sound / Waves and we hope to reach the vibration of Wisdom embedded Logic or Love Enlightened Intelligence transcending our microcosmic limitations understanding the macrocosms. Read more New Consciousness and Group Dynamics

Yggdrasil Tree of Life from Prose Edda, an Old Norse work of literature written in Iceland in the early 13th century. In 1847 painted by Oluf Olufsen Bagge
Those who follow Talmudic Jewish tradition do know יהוה or “Yahweh” to be the name of God; yet we all know that the word is substituted with a different term, so not to pronounce the name of God in vain.

The True Name of God Tetragrammaton scripts in Phoencian 1200 BC Paleo Hebrew 1000 BC and Hebrew 300 BC
Going back in time, while describing One & Only within the ancient Greece we find the use of:
1) IαΩ,
2) tetragrammaton יהוה in Hebrew as YHWH in Latin script and
3) kyrios read more about Esoteric teachings of Golden Citizens of Ancient Greece
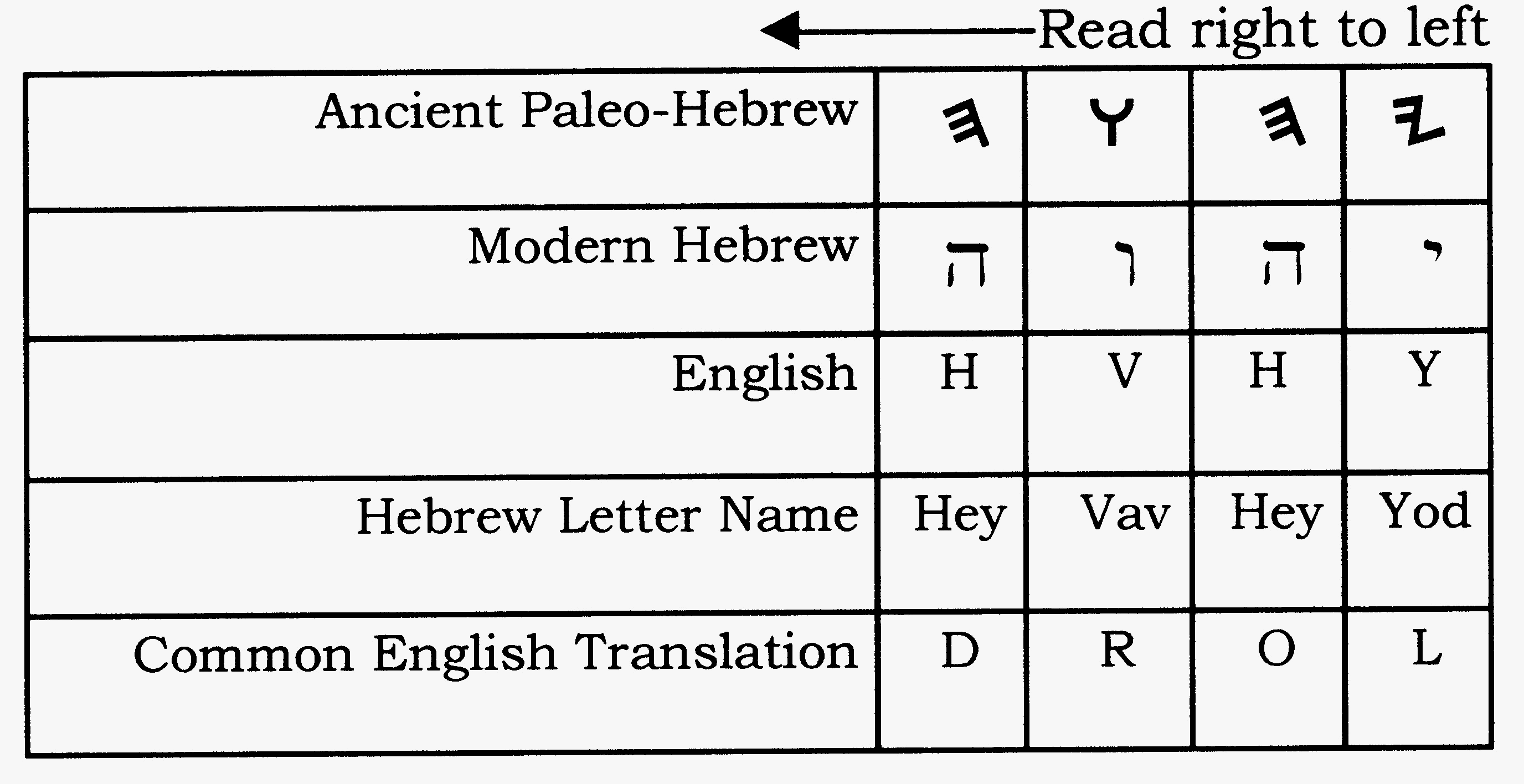
Tetragrammaton scripts, Anceint art, in Phoencian 1200 BC Paleo Hebrew 1000 BC and Hebrew 300 BC
consciousness, and the Book of the Dead
Did you know that the tetragram original home was Egypt?
Ancient Egypt Rosetta Stone
Ancient Egypt Sound Č (of Grčka or Greece, mačka or cat, China, or Chill, or Tao Te Ching) Frequencies Researching Ancient Egyptian 3 scripts (hieroglyphs, the sound based writing and Ancient Greek)...
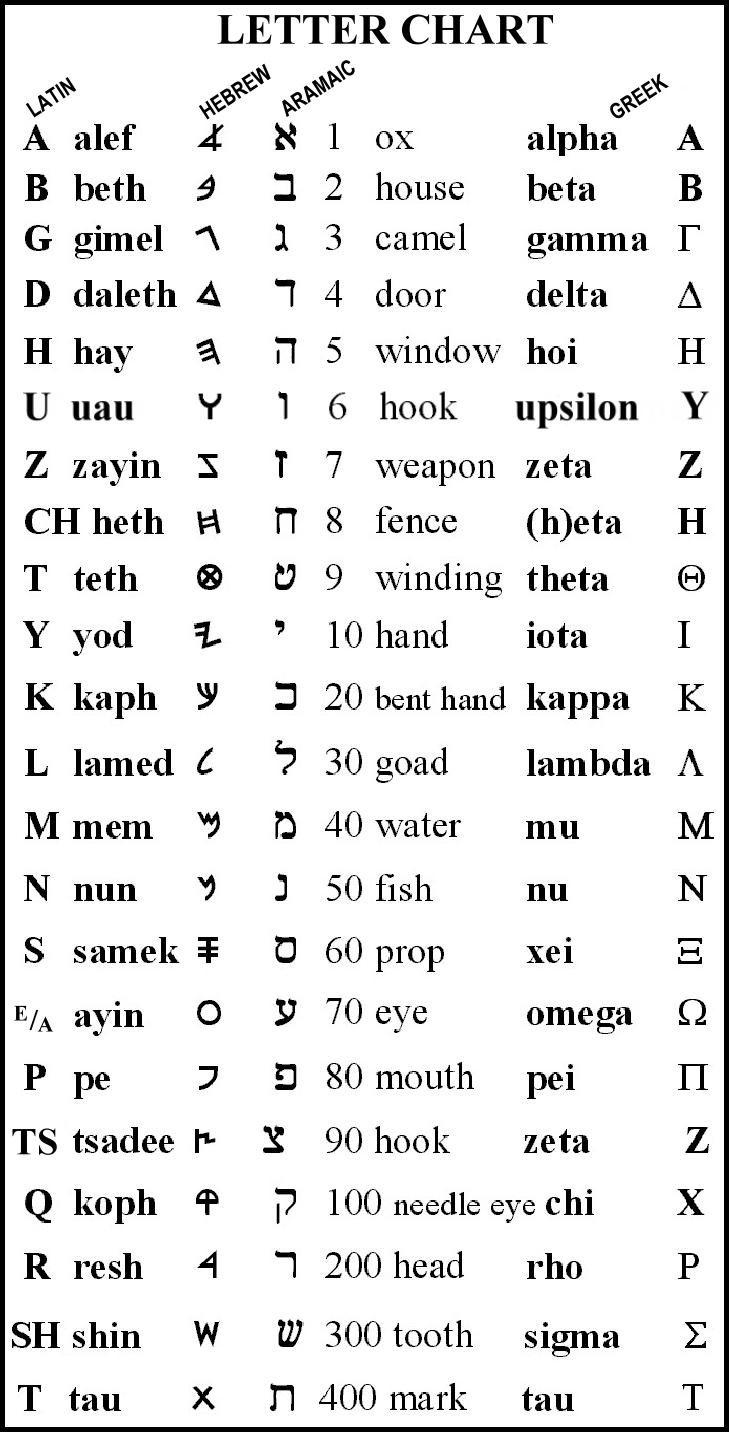
Ancient Egypt mystical knowledge and first alphabet letters chart Arabic Hebrew Greek
The oldest verified alphabet consists of 22 consonant letters, leaving vowel sounds implicit.
According to the Ancient Egyptian Myth the hieroglyphic script was invented by the God Thoth
We all remember the Egyptian hieroglyphs of some 1,000 distinct characters that were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt. Now, cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood, this is what researchers now call “the Proto-Canaanite alphabet”, the term used for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet. Again, lots of countries, governments, scientists, religion leaders wish to claim the invention of the alphabet because we all know how important it later became. Through the Phoenician alphabet's, the Greek and Aramaic scripts developed, the Latin and Cyrillic scripts evolved, and the Arabic and Hebrew scripts advanced.
We now know from the recently translated “Sinai inscriptions” 1480 BC that 22 Egyptian hieroglyphic symbols were borrowed to form the characters of the future alphabets.

Sinai inscriptions script 1845 BC
Handwriting the religious documents was known to our ancestors 1.000s of years ago.
A beautiful example was the compilation of the Book of the Dead. The Book of the Dead is an ancient Egyptian funerary text, also translated as Book of “Emerging Forth into the Light” is the loose collection of texts consisting of magic spells helping the dead King or Queen take the place amongst the gods, reuniting with divine father Ra. Written with ink and a reed brush on papyrus, or leather many famous recently excavated documents, such as the Papyrus of Ani, utilize it. It was also employed on wood for religious literature such as the Coffin Texts.
The Egyptians believed that knowing the name of something gave them power over it
The Egyptians believed that knowing the name of something gave them power over it, so the Book of the Dead gives the mystical names to the entities the soul would encounter in the afterlife, giving him or her power over them. Everyday magic made use of amulets in huge numbers.
Each Book of the Dead is custom-made and often the work of several different scribes and artists. Most sub-texts begin with the word ro, which can mean "mouth," "speech," "spell," or perhaps - "Word" or “Logos”. For the visual lovers, they were composed of sheets of papyrus joined together, the individual papyri varying in width from 15 cm to 45 cm. One source even gives us the price of the Book of the Dead scroll as one deben of silver, perhaps half the annual pay of a laborer.
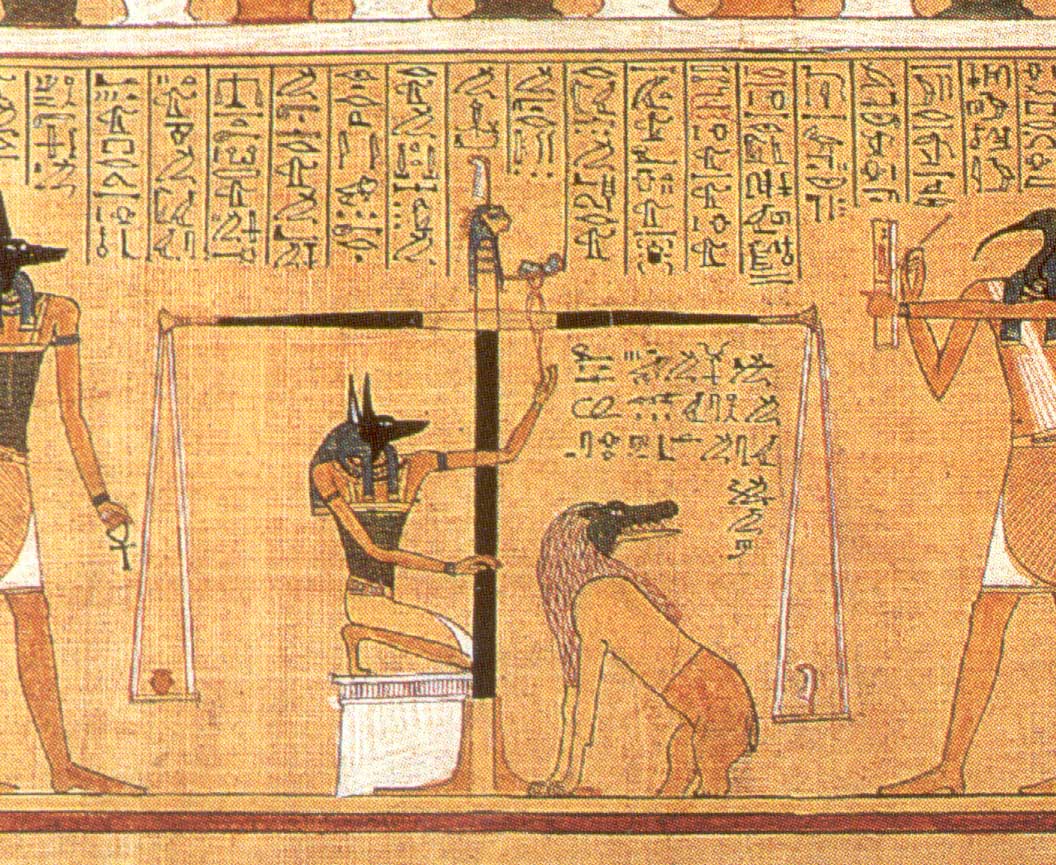
Weighing of the heart Egyptian Papirus in British Museum 1250 BC
A detailed scene, from the Papyrus of Hunefer 1285 BC, now in the British Museum, shows the heart weighed on the scale of Maat against the feather of truth, by the jackal headed Anubis. If his heart equals the weight of the feather he is allowed into the afterlife, if not, he is eaten by the devouring creatures: crocodile, lion, and hippopotamus.
One aspect of death was the disintegration of the various modes of existence.
- Mummification served to preserve and transform the physical body into its divine form
- Book of the Dead contained prayers recited so Soul does not linger but becomes one with Gods. The name of the dead was written in many places throughout the Book of the Dead with spells helping this afterlife journey
- the heart, included “Logos” and “Eros”, was protected with mystical words, sounds, psalms
- the ka, or dead-man’s spirit required offerings of food, water and incense,
- the ba depicted as a human-headed bird, that "goes forth by day"
- the shut, is the shadow of the King
If all the obstacles are past and the various modes of existence transformed, the dead person would “earn” life in the form of an akh, a blessed spirit with magical powers who dwells among the gods.
Facing Ma'at the dead person swore that he had not committed any sin from a list of 42 that refers to the ancient Egyptian concepts of “goodness” - truthfulness, law, morality, and justice.
Sinai Inscriptions Script 1845 BC

Egyptian religious script Papyrus Ani in Brigmen Art sample of the Book of Death
The finest of examples we have of the Egyptian Book of the Dead is the Papyrus of Ani, known as the Sinai, Ancient Egypt inscription dated 1480 BC. The carved texts on its temple to the Egyptian goddess Hathor and the Papyrus that is at the British Museum in London, was taken out of Egypt in 1888 by Sir E. A. Wallis Budge give us the most amazing insights.
For the history lovers this is the time line of the Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic writing:
3150 BC - First preserved hieroglyphs, on small labels found in the tomb of a king buried at Abydos
3000 BC - 2345 BC Royal pyramids contain the Pyramid Texts, carved specially for the Kings
2100 BC - 1st Coffin Texts, developed from the Pyramid Texts painted on the coffins of very wealthy influential citizens, regional governors and other high-ranking officials.
1600 BC - Earliest papyrus copies of the Book of the Dead are used instead of inscribing spells on the walls of the tombs
200 AC - Mummies buried with Greek texts of New and Old Testaments, and Ancient Greek Writers including Homer.
1798 – Napoleon is so intrigued by the mysticism of the Name of the supreme God, the Egyptian Zeus, wishing to learn about images, prayers and vibration - invades Egypt to excavate. Remembering Alexander the Great who did the same exploring Babylon Mysticism
Some believe to have found it in “All Seeing Eye” as a Masonic symbol of Deity
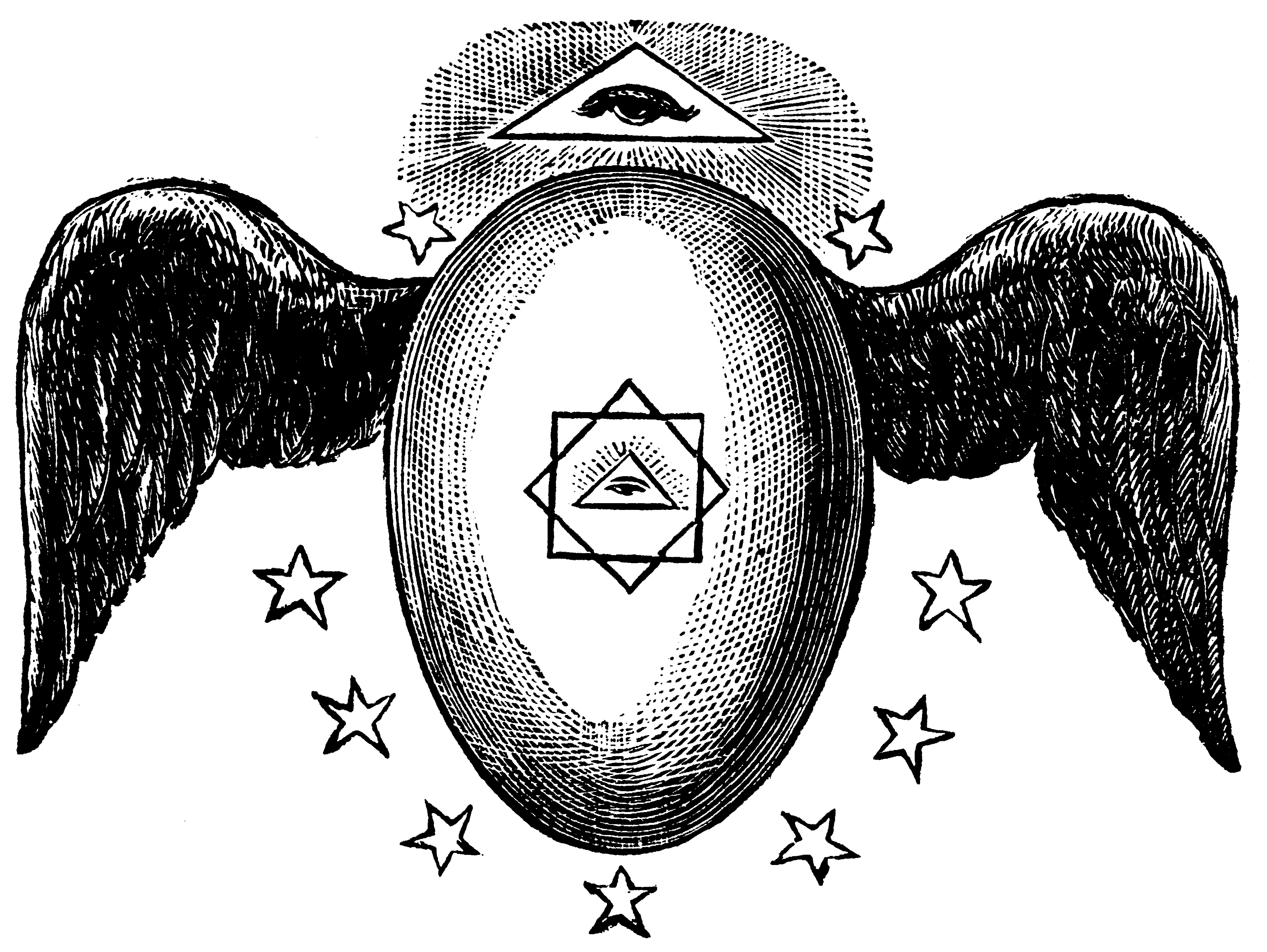
Kneph image Ancient and Primitive Rite of Masonry Kenneth MacKenzie
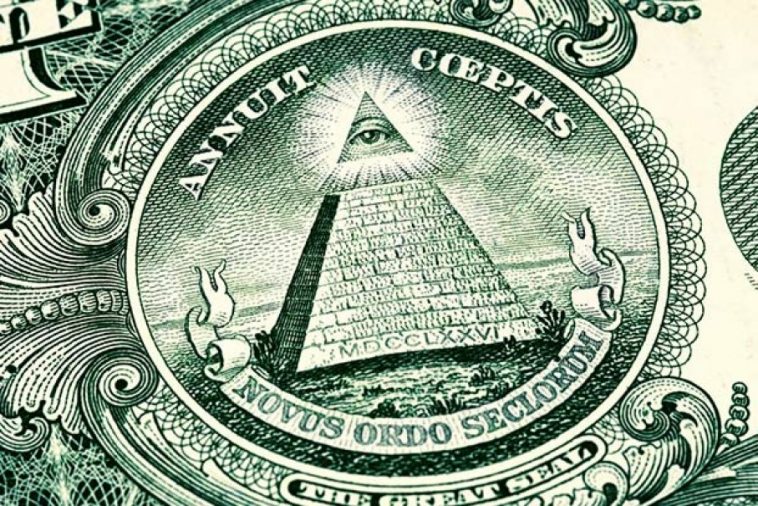

US dollar symbols the Great seal eye and pyramid
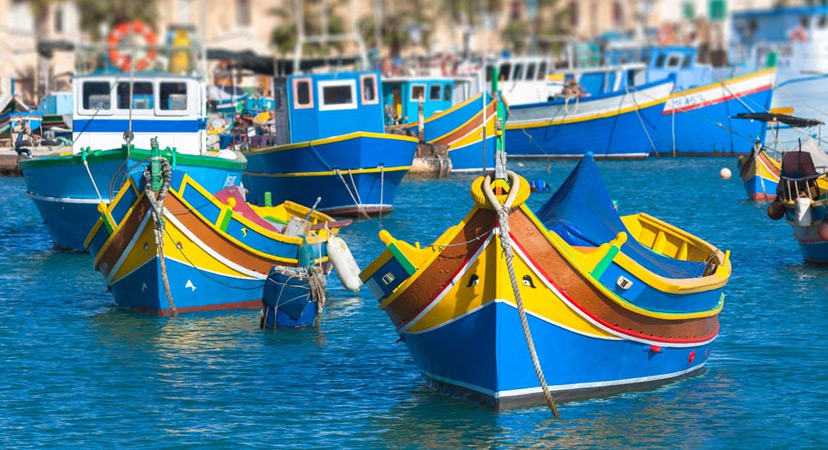

Fishermen Luzzu in Malta with Eye of Horus or Osiris used for protection.
Some other thought to have found it in Ankh

Some others believed it to be the ancient symbol of the Life Force
Unfortunately, we all still very well remember how fascinated people were seeing this symbol.







Metaphysics of sound No comments on Metaphysics of sound: